Inflammation in the Elbow: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
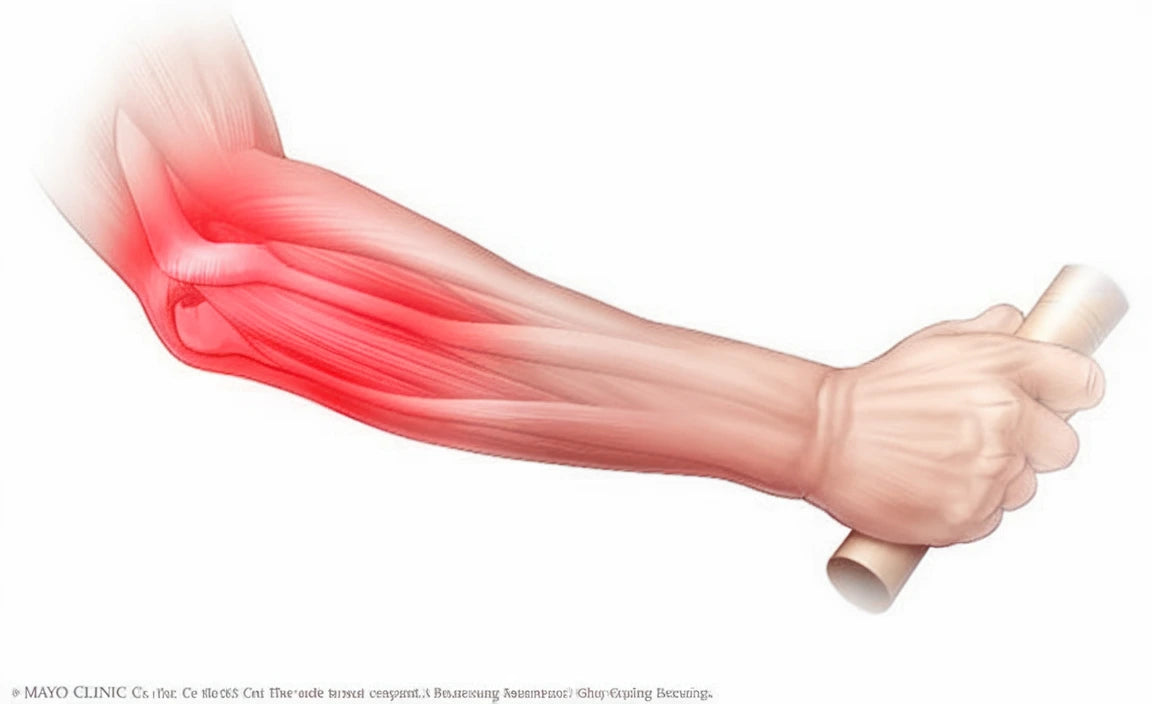
Elbow inflammation is a common problem that can cause pain and limited mobility. This article reviews the most common symptoms, causes, and treatment options for elbow inflammation.
Symptoms of inflammation in the elbow
Inflammation in the elbow can manifest itself in several ways, and the symptoms can vary in intensity. Common symptoms include:
- Elbow pain: This is often the most prominent symptom. The pain may be constant or worsen with movement and stress on the joint. The pain may occur on the outside of the elbow (tennis elbow), the inside (golfer's elbow), or around the entire elbow joint.
- Swelling: The area around the elbow can swell due to inflammation of the tissues. A swollen elbow may indicate bursitis or other inflammation.
- Stiffness: The elbow may feel stiff, especially in the morning or after extended periods of inactivity, which can affect mobility in the elbow joint.
- Redness and warmth: The inflamed area may become red and feel warm to the touch, which are typical signs of local inflammation in the elbow.
- Limited mobility: You may experience difficulty fully bending or extending your elbow and may have difficulty bending your arm normally.
- Tenderness to the touch: The affected area may be tender when pressed, especially over the tendon attachments or at the tuberosity on the inside and outside of the elbow.
- Pain in the elbow that may radiate into the forearm or up towards the upper arm.
- Pain during gripping movements involving the wrist and forearm.
Inflammation can make it painful to perform everyday activities such as lifting objects, turning handles, or even shaking hands. In the case of student elbow (olecranon bursitis), prolonged pressure on the back of the elbow can cause inflammation of the bursa.
Causes of inflammation in the elbow
Several factors can contribute to the development of inflammation in the elbow:
- Overuse: Repetitive movements or prolonged stress on the elbow can lead to inflammation. Tennis elbow and golfer's elbow occur due to overloading of the muscle and tendon attachments on the outside and inside of the elbow, respectively.
- Injury or trauma: A direct blow to the elbow or a fall can cause inflammation, including overextending the elbow or damage to the joint capsule.
- Infections: In rare cases, bacterial infections can lead to inflammation of the elbow, especially in the bursa (infectious bursitis).
- Underlying diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout can increase the risk of inflammation in the elbow. Arthritis can affect the inner and outer tendon attachments of the elbow.
- Age: With increasing age, the risk of inflammation in joints, including the elbow, increases due to changes in the structure of the tissues.
- Unilateral movements: Jobs or activities that require unilateral movements, especially if they involve the wrist, can cause overexertion and pain in the elbow (mouse arm).
- Sports injuries: Various sports injuries to the elbow can be caused by overuse, especially in sports such as tennis and golf, which require repetitive movements.
- Inflammation of the periosteum on the back of the elbow can occur from prolonged strain or direct pressure.
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) and golfer's elbow (medial epicondylitis) are two of the most common forms of inflammation of the elbow. Despite their names, you don't have to play tennis or golf to get them - they are caused by overuse of the muscles and tendons that attach to the elbow.
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammation of the elbow
Elbow inflammation is a common condition that is often caused by overuse, repetitive motion, or direct pressure on the joint. The pain can come on gradually or suddenly and worsen with movement. In order to achieve effective treatment, it is important to determine the cause and choose the right measures.
Rest and relief
Rest is one of the most important parts of treatment for elbow inflammation. Reducing stress and avoiding activities that aggravate the pain allows the tissues to recover. In some cases, a stabilizing elbow brace can be used to provide additional relief for conditions such as tennis elbow or golfer's elbow.
Cold and heat therapy
Cold is used to reduce swelling and pain in acute inflammation, while heat increases blood circulation and helps with stiffness. The combination of cold and heat can be used at different stages of recovery to optimize healing.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
If the pain is more severe, anti-inflammatory medications may be used. These reduce swelling, pain, and irritation in the tendons and muscles around the elbow. Medical treatment is often combined with other measures for long-term improvement.
Physiotherapy
Once the pain begins to subside, physiotherapy is a central part of rehabilitation. Specific exercises strengthen the muscles around the elbow, which improves mobility and prevents recurring problems. Treatment is tailored to the individual's needs and degree of discomfort.

How Elbow Support and Thermoreliever™ can help with elbow inflammation
Elbow supports and Termoreliever™ offer several benefits for people suffering from elbow inflammation:
- The elbow support provides support and relief to the inflamed elbow, which can reduce pain and improve stability. It is especially effective for tennis elbow and golfer's elbow by relieving the strain on the overworked muscles.
- The elbow support can help relieve the tendon attachments on both the outside and inside of the elbow, reducing strain during daily activities.
- Termoreliever™ offers both cold and heat therapy, which is important for managing inflammation and pain. Cold therapy can be used in the acute stage to reduce swelling, while heat therapy can be used later to increase blood circulation and promote healing.
- The combination of these products can help speed recovery by providing continuous support and pain relief for both tennis and golf elbow.
- In case of pain and problems in the elbow that are related to the wrist, a supplementary wrist support may be recommended to reduce the strain on the elbow.
- The products can be adapted to individual needs and used both during rest and light activity to reduce pain and support the healing process.
- For long-term problems with tennis arm or golf arm, the elbow support provides a relieving effect that can facilitate everyday activities.
Conclusion
Elbow inflammation can be painful and debilitating, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, most people can experience significant improvements. By combining traditional treatment methods with innovative aids such as Elbow Support and Termoreliever™, many people can effectively manage their symptoms and regain normal elbow function. It is important to listen to your body's signals and seek professional help if symptoms persist or worsen.
For long-term or recurring problems, it is recommended to consult a doctor or physiotherapist, especially if the inflammation affects daily activities or does not respond to self-care. Early intervention can prevent acute problems from developing into chronic conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does inflammation of the elbow usually last?
With the right treatment, many people can experience improvement within a few weeks. However, some cases can take longer, up to several months, depending on the severity. Tennis elbow and golfer's elbow can be long-term in some cases and require consistent treatment.
Can I exercise with inflammation in my elbow?
Light exercise and specific exercises can often be part of treatment, but it is important to avoid activities that aggravate the pain. Consult a physical therapist for a customized exercise program that can strengthen the muscles without increasing inflammation.
How do I use Termoreliever™ for inflammation in the elbow?
Use cold therapy in the acute phase to reduce inflammation, usually for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Then transition to heat therapy to promote healing and increase mobility once the acute phase has passed.
Can the Elbow Support prevent inflammation in the elbow?
Yes, by providing support and improving posture, the Elbow Brace can help reduce the risk of elbow strain and inflammation. It is especially useful during activities that put stress on the elbow, such as tennis, golf or working at a computer.
When should I seek medical attention for elbow inflammation?
Seek medical attention if the pain is intense, if you have significant swelling or redness, if you have a fever, or if your symptoms do not improve after a few days of self-care. If you have difficulty bending your arm or if the inflammation is severe, you should also contact your healthcare provider.

