Meniscus Injury: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
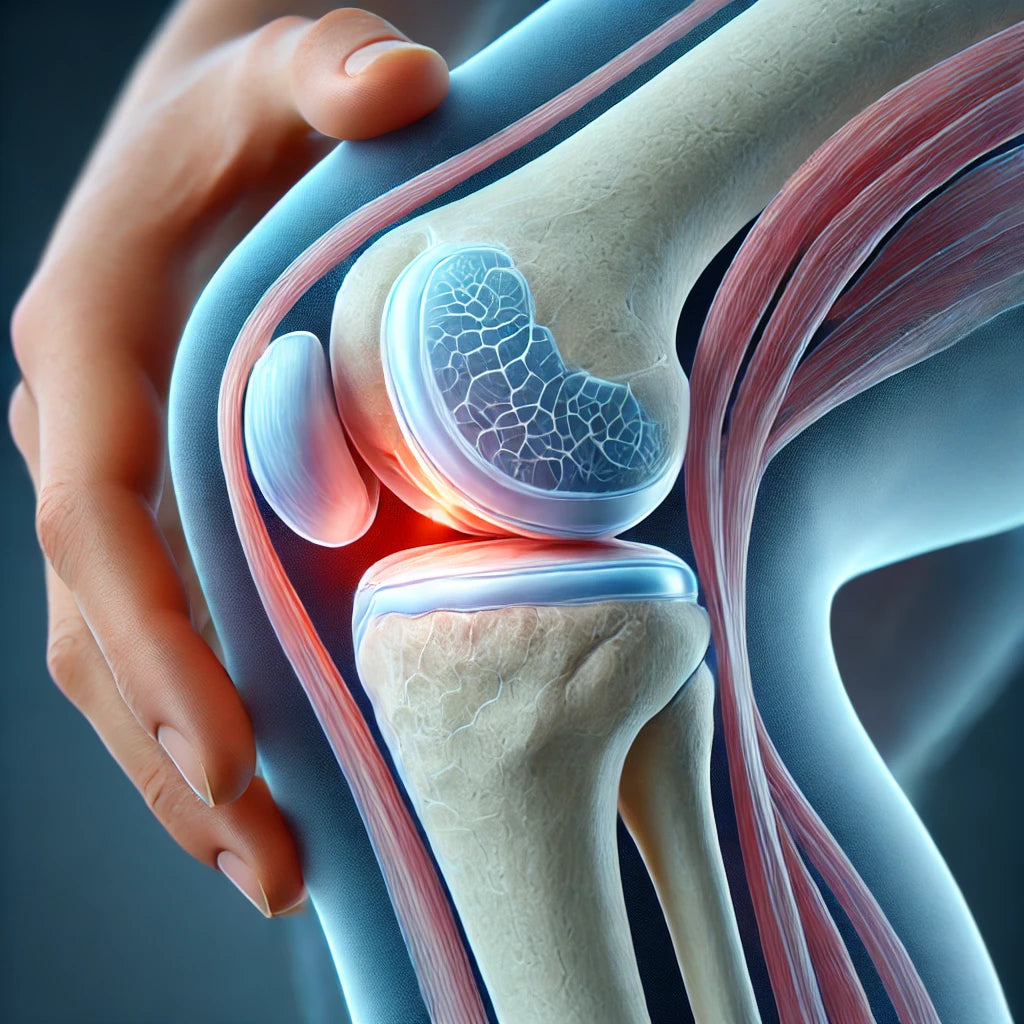
A meniscus tear is one of the most common knee injuries and can cause significant discomfort, pain and limited mobility. Meniscus tear knee problems affect many people every year. Whether you exercise or play sports regularly or just have an active lifestyle, it is important to understand what a meniscus tear is, how it is diagnosed and what treatment options are available for meniscus tears. In this article, we will go over everything you need to know about meniscus tears, including how specialized knee braces can support your rehabilitation and rehab after the injury.
What is a Meniscus Injury?
The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage disc in the knee that acts as a shock absorber between the thighbone and the lower leg. There are two menisci in the knee joint – an inner (medial meniscus injury affects this part) and an outer. The menisci are two discs of cartilage that help to distribute the load in the knee and provide stability to the joint.
A meniscus injury occurs when this cartilage disc is damaged or torn, often due to:
- Twisting or straining the knee (e.g. during sports or unusual movements)
- Degenerative meniscus damage due to wear and tear over time (common in older people)
- Trauma or acute injuries (e.g. falls or accidents)
Meniscus problems can be of different types. The type of meniscus injury often depends on how the injury occurred and where in the meniscus the injury is located. Meniscus injury most often occurs when the knee is bent and subjected to twisting. Acute meniscus injury is more common in younger people and often occurs during rapid movements and activities that involve twisting while the knee is under load. Degenerative meniscus injury more often affects older people and is due to wear and tear over time.
Symptoms of Meniscus Injury
Meniscus tear symptoms vary depending on the type of injury and its severity. If you have suffered a meniscus tear, you may experience some or all of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the knee, especially when twisting, bending, or straining
- Swelling around the knee joint, often within 24 hours of the injury
- Locking in the knee or a feeling that it is "stuck" in certain positions, making it difficult to fully extend the knee
- Instability or a feeling that the knee is "giving way"
- Reduced mobility and difficulty extending the knee or bending it fully
- Tenderness when pressing on the inside of the knee in case of medial meniscus injury
- Pain and sometimes a clicking sound when you put weight on the knee
Meniscus injury – symptoms can develop gradually in degenerative injuries or appear suddenly in acute injuries. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention and not ignore them. An untreated meniscus injury can lead to long-term problems, including osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
Diagnosis of Meniscus Injury
If you suspect a meniscus injury, you should consult a doctor or orthopedic surgeon. To determine a meniscus injury, doctors usually use the following diagnostic methods:
Physical Examination
The doctor may perform specific tests such as the McMurray test to assess the stability and mobility of the knee. This test helps identify damage to the meniscus.
Discussion about Symptoms and Injury
A detailed description of how the injury occurred and what symptoms you are experiencing is important for diagnosis.
Imaging diagnostics
- MRI: Provides detailed images of the soft tissues of the knee, including the menisci
- X-ray: Used to rule out bone fractures or other injuries
A correct diagnosis is crucial to determining appropriate treatment for meniscus injury and to rule out other potential problems that may occur simultaneously, such as injuries to both the meniscus and ligaments.
Treatment of Meniscus Injury
Treatment for a meniscus tear depends on the severity, type, and location of the injury, as well as your age and activity level. Treatment may include both nonsurgical and surgical methods:
1. Non-Surgical Treatment
- Rest and Relief: Avoid activities that put stress on the knee to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatories can relieve pain and swelling.
- Physical therapist: An expert can help you with an individually tailored exercise program to improve the strength and balance of your knee.
It is important to exercise during recovery to rebuild strength and mobility in your knee. Your physical therapist can guide you through appropriate exercises to strengthen the muscles around your knee and restore stability.
2. Surgical Treatment
In more serious injuries to the meniscus, especially if the knee locks or if there are loose parts of the meniscus, arthroscopic meniscus surgery may be necessary. During the procedure, all or part of the damaged meniscus tissue is repaired or removed.
Meniscus injuries can heal without surgery in some cases, especially if the injury is in the outer parts of the meniscus where the blood supply is better. Orthopedic surgery is usually considered when conservative treatment does not provide sufficient improvement after 6-8 weeks, or if the injury is extensive to begin with.
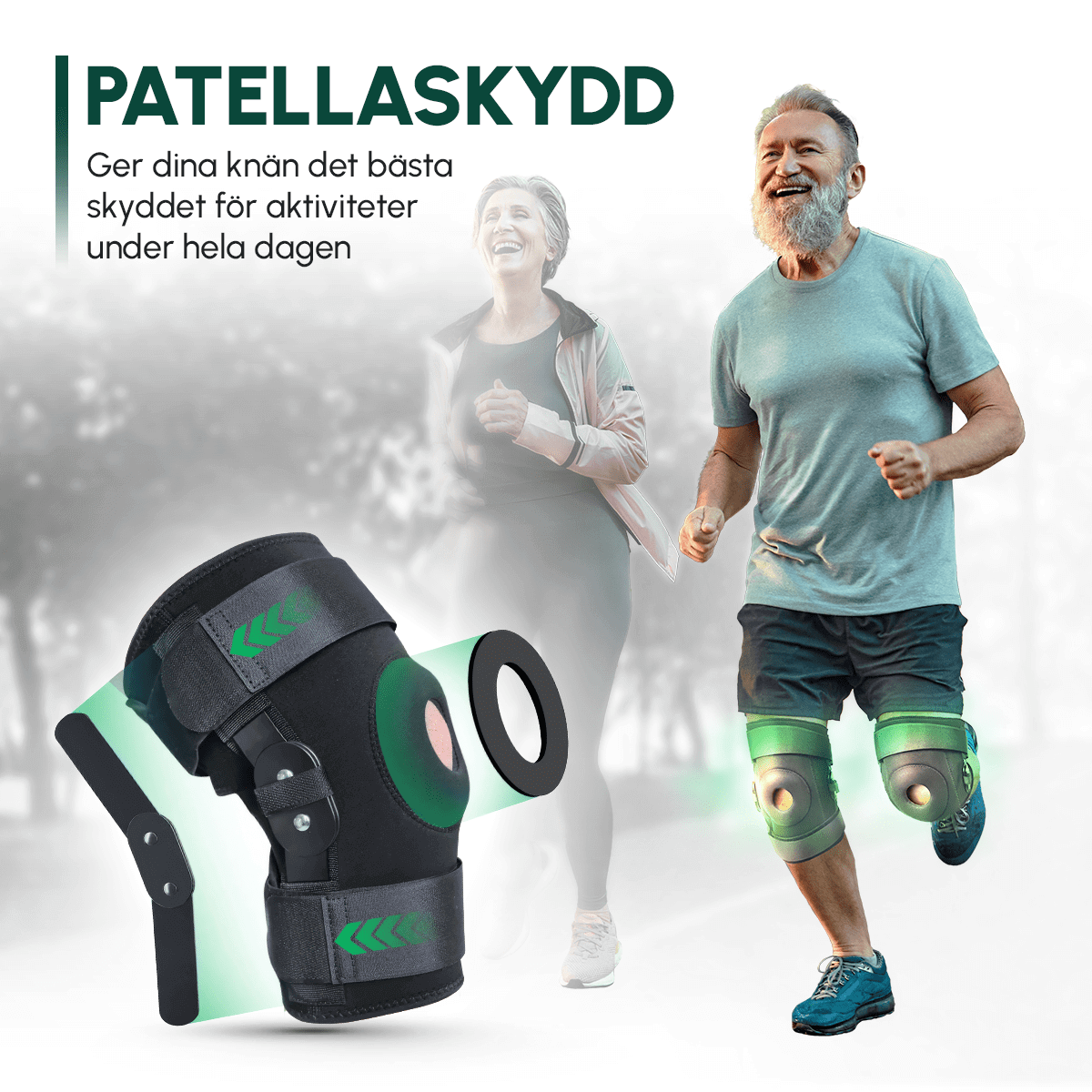

How Knee Pads for Meniscus Injury Can Help
During recovery from a meniscus injury, a specially designed knee brace can be an invaluable asset. Here are some of the benefits:
- Compression: Reduces swelling and increases blood circulation for faster healing
- Support and Stability: Helps stabilize the knee joint during daily activities and exercise
- Preventive Protection: Reduces the risk of further injuries during rehabilitation
- Increased Comfort: Provides pain relief and makes it easier to regain mobility without discomfort
- Shock-absorbing effect: Relieves pressure on the damaged meniscus
Using a knee brace during recovery can potentially speed up the healing process and allow you to return to your normal activities more quickly. This is especially important to avoid an increased risk of osteoarthritis in the future.
Buy nowConclusion
A meniscus tear can be painful and limiting, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis is usually good. By paying attention to symptoms and seeking care early, you can reduce the risk of long-term problems.
After any surgery, regular exercise is essential to rebuild strength and balance in the knee. Rehab under the guidance of a physiotherapist provides the best results. You can also seek help from specialist clinics that focus on knee problems.
Using specialized knee braces can provide additional support and comfort during recovery. Whether you choose conservative treatment or surgery, it is important to follow the advice of your doctor and physical therapist for a safe and effective rehabilitation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do I know if I have a meniscus injury?
Typical signs include pain, swelling, locking, and instability of the knee. A doctor or orthopedist can provide a definitive diagnosis through clinical examination and possible imaging.
Can a meniscus injury heal on its own?
Minor injuries can sometimes heal with rest and conservative treatment. It may be worth seeing if the symptoms resolve after a few weeks of rest and decompression before considering more invasive measures. Injuries to the outer parts of the meniscus have a better blood supply and therefore a better ability to heal.
How long does it take to recover from a meniscus injury?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment method, but can take from a few weeks to several months. It is important to complete the entire rehabilitation period to restore full function and reduce the risk of recurring problems.
Can I exercise with a meniscus injury?
Light exercise can often be done under the supervision of a physical therapist, but avoid activities that aggravate symptoms. By exercising properly, you can actually speed up healing and increase knee stability.
How can Knee Pads for Meniscus Injury help?
aThe knee brace provides support and stability to the knee, reduces pain and swelling, and improves comfort during daily activities and rehabilitation. It can be especially valuable during the return to sports and other physical activities.effective with conservative methods and lifestyle changes.

