Contusion in the Elbow: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
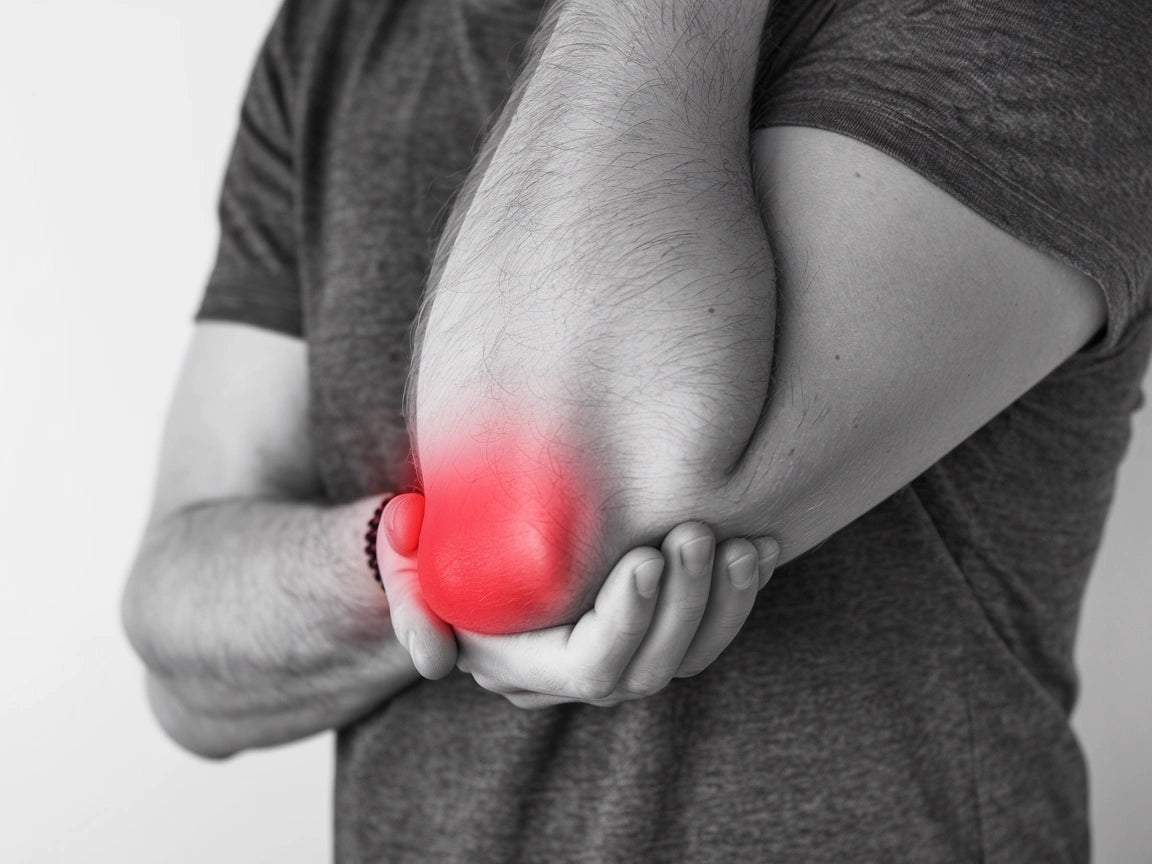
Elbow pain is a common problem that can have many different causes, from overuse to inflammation. This article reviews the most common causes, symptoms, and treatment options for elbow pain.
Symptoms of elbow pain
Elbow pain can manifest itself in several ways and vary in intensity. Common symptoms include:
- Elbow pain: This can be a constant, dull ache or a sharp pain with certain movements. It often hurts when you bend and straighten your elbow joint.
- Pain radiating into the hand: Some types of elbow problems can cause pain that radiates down the forearm and hand. This is especially common with tennis elbow, where the pain is on the outside of the elbow.
- Stiffness and limited mobility: It may be difficult to fully bend or straighten your elbow, which can affect your ability to use your arm normally.
- Tenderness to the touch: Especially around the "knob" of the elbow or on the inside or outside. With tennis elbow, the outside of the elbow is tender, while with golfer's elbow, the inside of the elbow is painful.
- Arm weakness: It may be difficult to grasp or lift objects with your hand and arm due to pain in the elbow area.
- Inflammation and swelling: The elbow may feel warm and look swollen, especially with conditions such as bursitis or elbow bursitis.
Causes of elbow pain
Several factors can contribute to the development of elbow pain:
- Overuse: Repetitive movements, especially during weight training, tennis, golf, or one-sided work, can lead to overuse of muscles and tendons. This is one of the common causes of elbow pain.
- Injuries: Direct blows, falls, or twists can damage the structures of the elbow, such as the joint capsule or tendon attachments. An overextended elbow can occur from trauma or overexertion.
- Inflammation: Conditions such as tennis elbow or golfer's elbow are caused by inflammation of the muscle attachments. Tennis elbow and golfer's elbow occur due to overuse and one-sided movements.
- Nerve compression: Pressure on nerves that pass through the elbow can cause pain and numbness that radiates into the forearm.
- Arthritis: Degradation of joint cartilage can lead to pain and stiffness in the elbow joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa around the elbow can cause pain and swelling. Student's elbow is a form of bursitis that can occur in the bony sac at the back of the elbow after prolonged pressure.
- Mouse arm: Repetitive movements during one-sided work, such as computer work, can lead to elbow pain due to overexertion of the muscles.
- Stretching or overstretching: Sudden movements can cause stretching of the muscles or ligaments of the elbow.
Diagnosis and treatment of elbow pain
Elbow pain often occurs due to overuse, repetitive movements, or inflammation of muscles and tendons.
Common causes include tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, or strains. To treat the problem effectively, it is important to determine the cause and choose the right combination of rest, exercise, and support.
Rest and relief
Resting from strenuous movements is often the first step in reducing pain and inflammation in the elbow.
Advantages of elbow support: Provides support and reminds you to avoid overexertion during everyday activities.
Physical therapy
Movement and strength exercises improve blood circulation and help restore function in the arm.
A physical therapist can design a program of stretching and strength exercises tailored to the cause of the pain.
Advantages of elbow support: Supports the elbow during exercise and promotes safe and controlled movement.
Pain relief
Anti-inflammatory drugs or painkillers can be used temporarily to relieve pain.
Advantages of elbow supports: Can reduce the need for medication by naturally relieving pressure on the area.
Cold and heat treatment
Cold reduces inflammation and swelling, while heat can increase blood flow and reduce stiffness in the elbow.
Advantages of elbow supports: Complements treatment by keeping the area stable and reducing strain during recovery.
Important to consider
Proper treatment of elbow pain helps prevent the condition from becoming chronic.
With the help of a physical therapist, you can get an exercise program that strengthens muscles and improves mobility, while the Elbow Support contributes to stability and pain relief in everyday life.
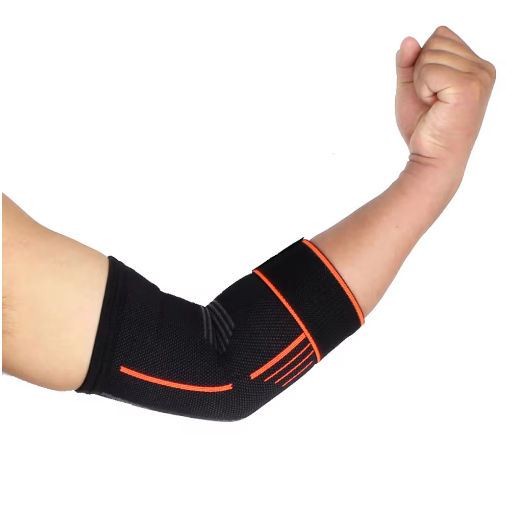
How Elbow Support can help with elbow pain
The elbow support offers several benefits for people suffering from elbow pain:
- Provides support and stability to the affected elbow, which can reduce pain during painful movements.
- Helps distribute pressure evenly across the joint, which can reduce pressure points and irritation.
- Can be used during daily activities and training to provide continuous support and reduce overload.
- Supports rehabilitation exercises and can help maintain joint mobility.
- Prevents further injury by limiting extreme movements that can aggravate the condition.
- Provides relief for both tennis elbow, which is on the outside of the elbow, and golf elbow, which is on the inside of the elbow.
Elbow supports are a valuable aid for relieving pain on the outside or inside of the elbow. They can be used in combination with other treatment methods to speed up healing.
Buy NowConclusion
Elbow pain can be a frustrating and limiting problem, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, most people can experience significant improvement. By combining rest, physical therapy, and the use of supportive devices like the Elbow Brace, many people can effectively manage their symptoms and return to normal activities. It is important to listen to your body's signals and seek professional help if the pain persists or worsens.
Most cases of tennis elbow or golfer's elbow get better within a few weeks to months with proper treatment and adequate rest. Although tennis and golf are known to cause these conditions, tennis elbow can also be caused by many other activities that involve repetitive motion of the wrist and elbow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does it take for an elbow contusion to heal?
The duration varies depending on the cause, but with the right treatment, many people can experience improvement within a few weeks to months. Chronic conditions may take longer to heal.
Should I seek medical attention for an elbow contusion?
It depends on the cause and the intensity of the pain. Light exercise and specific exercises can often be beneficial, but consult a physiotherapist for a customized program. Avoid movements that aggravate the pain.
How do I use Termoreliever™ for an elbow contusion?
Seek medical attention if the pain is intense, persistent, or if you experience significant swelling, redness, or limitation in mobility that does not improve with self-care.
Can I exercise with an elbow contusion?
Yes, the Elbow Support can be used preventively during activities that put strain on the elbow, especially for people who have previously had problems or who perform repetitive movements at work or during leisure activities.
How do I prevent future elbow contusions?
Tennis elbow causes pain on the outside of the elbow, while golfer's elbow causes pain on the inside. Both are caused by overuse of muscle attachments but affect different muscle groups.

