Apophyseitis (Sever's Injury): Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
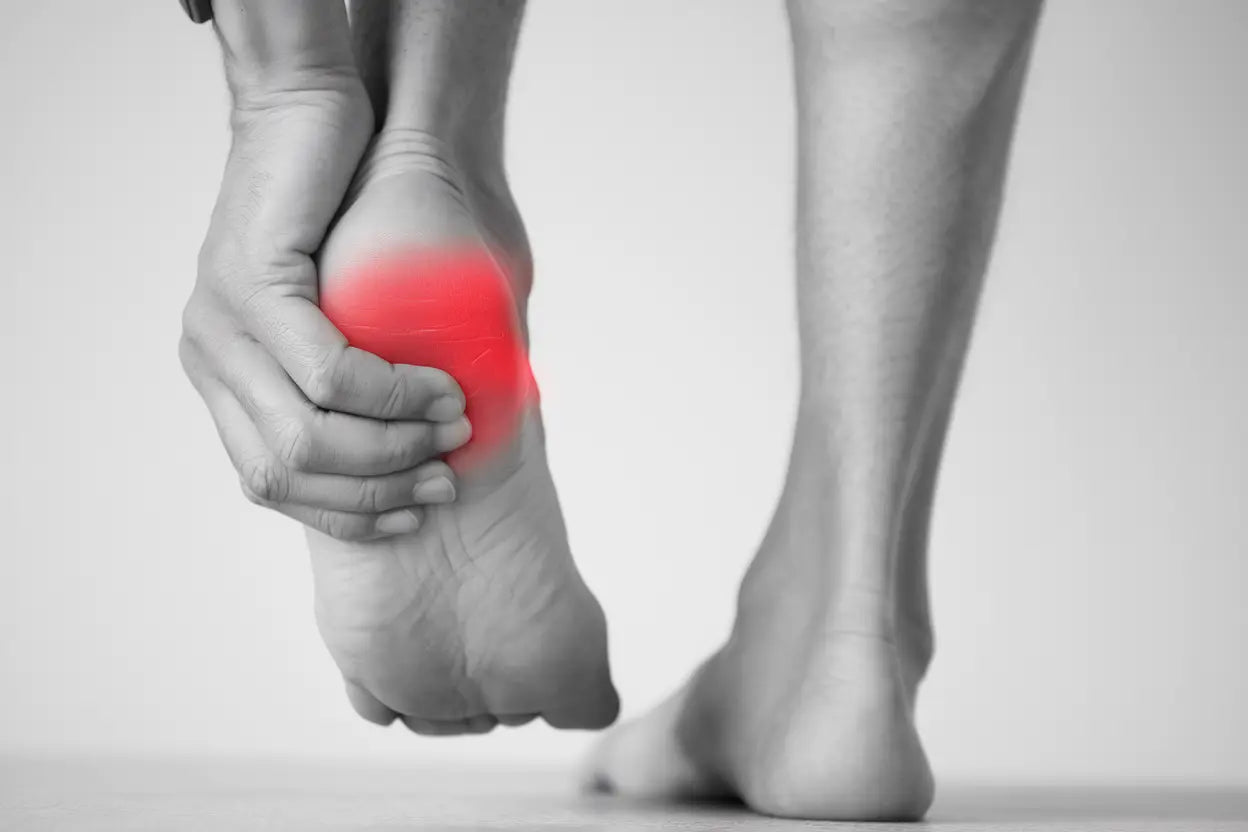
Apophysitis in the heel, also known as Sever's injury, is a common cause of heel pain in growing children and adolescents. This article discusses the most common symptoms, causes, and treatment options for this condition.
Definition and Background: What is Apophysitis (Sever's Injury)?
Apophysitis is an inflammation of the growth plate in the heel bone, which often affects active children and adolescents during growth spurts. Calcaneal apophysitis (the medical term for Sever's injury) is one of the most common causes of heel pain in children. This condition is classified under ICD-10 as calcaneal apophysitis (ICD 10 code M92.8). The condition occurs when the growth plate in the heel bone (calcaneus) becomes irritated and inflamed, often due to overuse when weight is placed on the heel.
Symptoms and Issues: How to Recognize Sever's Injury
Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the heel, especially after physical activity
- Tenderness when pressure is applied to the back of the heel
- Swelling around the heel
- Limping or difficulty walking on tiptoes
- The pain may worsen during running or jumping
Apophysitis in the heel in children can make it painful for them to walk or run. The pain is usually located at the back edge of the heel, where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone. Many children describe it as feeling like someone is squeezing their heel, and the pain typically worsens with activity and eases with rest.
Causes and Risk Factors Behind Apophysitis (Sever's Injury)
Several factors can contribute to the development of Sever's injury:
- Rapid growth during puberty
- Overuse from intense physical activity
- Tight calf muscles
- Improper foot positioning or biomechanics
- Hard or inappropriate shoes
Apophysitis of the foot and apophysitis of the hip are similar conditions affecting other parts of the body, but apophysitis of the heel is the most common form in children. This overuse injury occurs when the tendon that attaches to the heel bone pulls on a growth plate, causing inflammation. The injury is essentially harmless but can cause significant discomfort for a child if not treated.
Diagnosis, Investigation, and Treatment: Steps Towards Recovery
| Diagnosmetod | Behandlingsalternativ | Fördelar med TåKomforten™ |
|---|---|---|
| Fysisk undersökning | Anpassade skor och inlägg | Avancerad justeringsbehandling |
| Röntgen | Smärtlindrande läkemedel | Gradvis lindring av inflammation |
| Gånganalys | Fysioterapi och övningar | Icke-invasivt alternativ |
| MRI vid behov | Kirurgi i svåra fall | Kan användas dagligen för kontinuerlig behandling |
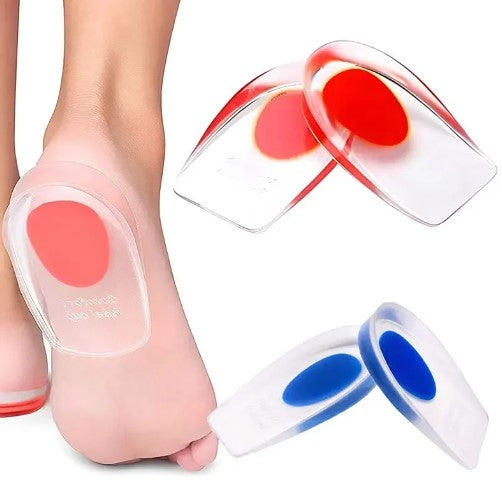

Assistive Devices and Product Choices: How Heel Cups (Tulis) Relieve Sever's Injury
Heel cups from Komforten offer several benefits for those with Sever's injury:
- Provides extra cushioning and relief for the heel
- Helps reduce pressure on the inflamed area
- Can be used in various types of shoes for consistent support
- Enhances comfort during daily activities and sports
- Made from high-quality materials for optimal shock absorption
When the heel is relieved with heel cups, the traction on the inflamed growth zone decreases, creating better conditions for healing. Many children can continue their activities while wearing heel cups in their shoes, making this a popular and effective treatment option.
Buy nowConclusion: Summary and Ongoing Care
Apophysitis (Sever's injury) is a common cause of heel pain in growing children and adolescents, but with the right treatment and support, most can return to normal activity without long-term issues. The use of heel cups, along with activity modification and stretching, can effectively relieve symptoms and support the healing process. It is important to consult a doctor or foot specialist for an accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does Sever's injury usually last?
Severs injury is self-limiting and usually resolves when growth is complete, which can take a few months up to a couple of years.
Can my child continue with sports during the treatment of Sever's injury?
Some activity modification is often recommended, but total rest is rarely necessary. Consult a doctor for individual recommendations.
How to Use Heel Cups Correctly?
Place the heel cup in the shoe so that the heel rests centered in the cup. They can be used in most types of shoes.
Can Severs' injury be prevented?
While it may not always be completely preventable, regular stretching, wearing appropriate shoes, and using heel cups can help reduce the risk.
When should I seek medical care for my child's health pain?
If the pain is persistent, worsens over time, or affects the child's daily activities, you should consult a doctor.
