ACL Injury: Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury - Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
An anterior cruciate ligament injury, also known as an ACL injury (Anterior Cruciate Ligament in English, acl Swedish: förstärke korsband), is one of the most common serious knee injuries. This type of injury affects the stability of the knee joint and can have significant consequences for a person's mobility and athletic activities. In this article, we will review what an ACL injury is, its causes, symptoms and treatment options.
What does an anterior cruciate ligament injury mean?
The ACL, or anterior cruciate ligament, is one of the four major ligaments in the knee joint. It crosses the knee diagonally and plays a crucial role in the stability of the knee joint. An anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs when this ligament is stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. The injury is always classified as serious because it affects the passive stability of the knee joint and creates instability in the knee.
Understanding what an ACL injury is means you need to know the anatomy of the knee. The anterior cruciate ligament is located inside the knee joint and connects the thighbone (femur) to the lower leg. Together with the posterior cruciate ligament, which runs in the opposite direction, they form a cross that stabilizes the knee joint forward, backward and in rotation. When the anterior cruciate ligament is injured, the knee loses a significant amount of its stability, especially during rotational movements. Read more about cruciate ligament injury here .
Common causes of ACL injuries
ACL injuries are often caused by sudden movements or traumatic force to the knee. Common causes include rapid changes in direction while running, sudden stops, improper landing after a jump, or direct impact to the knee. These anterior cruciate ligament injuries are particularly common in high-intensity sports such as soccer, handball, and alpine skiing.
Anterior cruciate ligament injuries are more common in women than in men, possibly due to anatomical and hormonal differences. The injury often occurs without contact with another player, usually when the leg is twisted while the foot is fixed on the ground. In some cases, the posterior cruciate ligament can also be injured at the same time, which further worsens the instability of the knee. Please also read about posterior cruciate ligament injury .
How do you recognize symptoms of anterior cruciate ligament injury?
The most common symptoms of an ACL injury include:
- An audible "pop" or the feeling of something breaking in the knee at the time of injury
- Severe pain and inability to continue activity
- Rapid swelling of the knee (hemarthrosis) which often occurs within a few hours
- Reduced mobility in the knee joint
- Feeling of instability, especially when trying to twist or turn the knee
When the anterior cruciate ligament is injured or damaged, the knee can swell significantly. The swelling, which is caused by bleeding into the joint (hemarthrosis), can make it difficult to fully bend or straighten the knee. The acute pain usually subsides after a few days, but the feeling of instability remains. Many people describe it as the knee "giving way" or feeling unsteady, especially when changing direction or going up stairs. Read more about unstable knee .
Diagnosis and treatment options
If you suspect an ACL injury, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Your doctor may refer you to an orthopedic surgeon for further evaluation. Diagnosis is usually made through a combination of a physical examination and imaging tests such as an MRI.
Treatment for an ACL injury depends on the extent of the injury and the individual needs of the patient. Surgery may be necessary if the injury is severe or if the patient is active in sports. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries that do not require surgery are treated conservatively with physiotherapy and rehabilitation. For those who undergo surgery, extensive rehabilitation is required after surgery.
A cruciate ligament reconstruction is a surgery in which the damaged cruciate ligament is replaced with a new cruciate ligament, usually using a tendon from the patient's own leg. This procedure is usually performed arthroscopically (keyhole surgery) and requires the use of crutches for a limited period afterwards. The goal of the surgery is to restore the stability of the knee and prevent further damage to the meniscus and cartilage. Also read about meniscus injuries that often occur together.
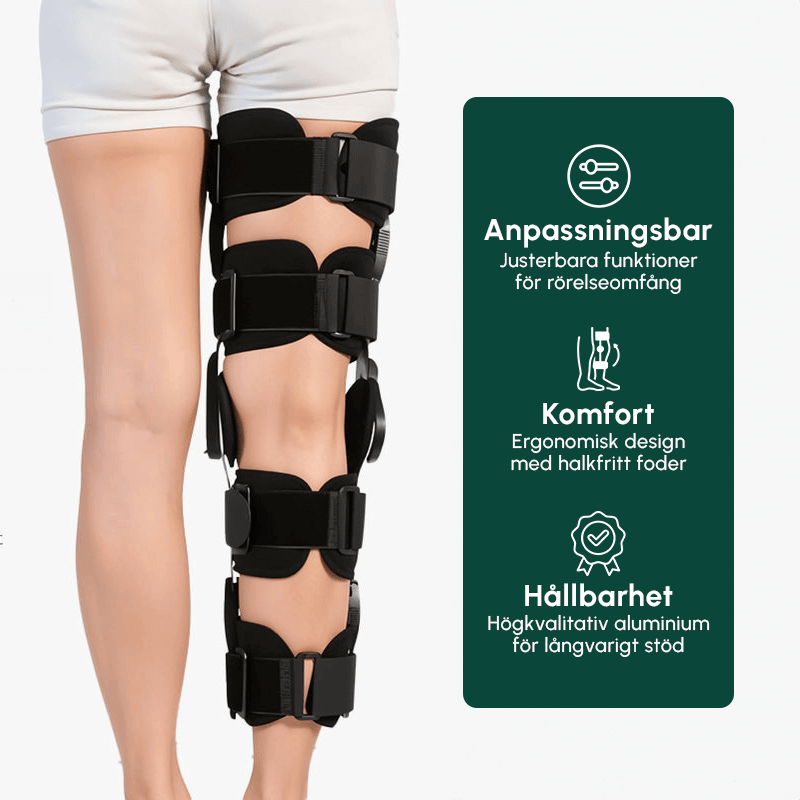
Benefits of knee pads for ACL injuries
A quality cruciate ligament injury knee brace can be a valuable aid in rehabilitation and prevention of further injuries. Here is a comparison of the benefits:
- Benefit Description
- Increased stability Provides extra support to the knee joint
- Reduced risk of overstretching Limits extreme movements
- Improved proprioception Increases body awareness
- Increased security Provides confidence when returning to activity
- Customizable compression Helps control swelling
The knee brace is designed to provide optimal support without restricting movement unnecessarily, making it suitable for both rehabilitation and continued sports after an anterior cruciate ligament injury. It can be especially useful during the period when the new cruciate ligament is healing and knee function is not yet fully restored. Find out more about training after a knee injury here.
Buy nowACL rehabilitation and recovery
Rehabilitation is a central part of treatment regardless of whether the anterior cruciate ligament injury is operated on or not. A well-planned rehabilitation aims to restore the function, strength and stability of the knee joint. After surgery, rehabilitation is particularly important to ensure that the new cruciate ligament is fully integrated and functions properly.
A structured exercise program led by a physiotherapist focuses on:
- Reduce swelling and pain
- Restoring range of motion in the knee
- Strengthen the muscles around the knee, especially the thigh muscle
- Improve balance and coordination
- Gradual return to sports and physical activity
Rehabilitation after an ACL injury takes time, usually 6-12 months before full return to sports is possible. During this period, it is important to follow the training program carefully and not rush back to high-intensity activities before knee function is restored.
How to prevent anterior cruciate ligament injuries
To reduce the risk of ACL injuries, it is recommended:
- Strength training for legs and torso, with a particular focus on hamstrings and quadriceps to balance muscle strength around the knee
- Improved landing technique and movement awareness, especially practicing landing with bent knees
- Balance and coordination exercises that improve body control
- Regular stretching and mobility training, especially for thigh and hip muscles
- Use of shock-absorbing shoes appropriate for the sport in question
- Gradually increase training intensity to give the body time to adapt
Conclusion
An anterior cruciate ligament injury is a serious knee injury that requires careful diagnosis and treatment. With proper care, including surgery if necessary, physical therapy, and the use of supportive devices such as cruciate ligament knee braces, most people can return to their normal activities. However, it is important to follow the rehabilitation plan carefully and be patient during the healing process. Read more about dislocated knees .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long is the recovery time after an ACL injury?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment method chosen. With conservative treatment, it can take 3-6 months before you can return to full activity. After surgical reconstruction, rehabilitation can take 6-12 months before you can return to sports at the same level as before the injury. It is important to follow the advice of the physiotherapist and not rush the process to avoid relapse.
Can I exercise with an ACL injury?
Yes, but it is important to adapt training to the injury. During the acute phase, focus should be on reducing swelling and regaining mobility. After that, strength training and balance exercises can be gradually introduced under the supervision of a physiotherapist. Activities that involve rapid twisting or jumping should be avoided until the knee is fully rehabilitated. Using a knee brace such as the Knee Guard for ACL Injury can provide extra support and security during training.
How effective is Knee Support for Cruciate Ligament Injury in preventing ACL injuries?
Knee braces for ACL injuries can be an effective tool in reducing the risk of ACL injuries, especially when returning to sports after a previous injury. They provide additional stability to the knee joint and can help prevent overextension. However, it is important to remember that a knee brace is not a substitute for proper training and technique. It should be used as part of a comprehensive prevention strategy that includes strength training, balance exercises, and proper warm-ups. Always consult a doctor or physical therapist for personal recommendations on the use of knee braces.

