Knee Ligament Injury: Symptoms, Treatment, and the Right Knee Support
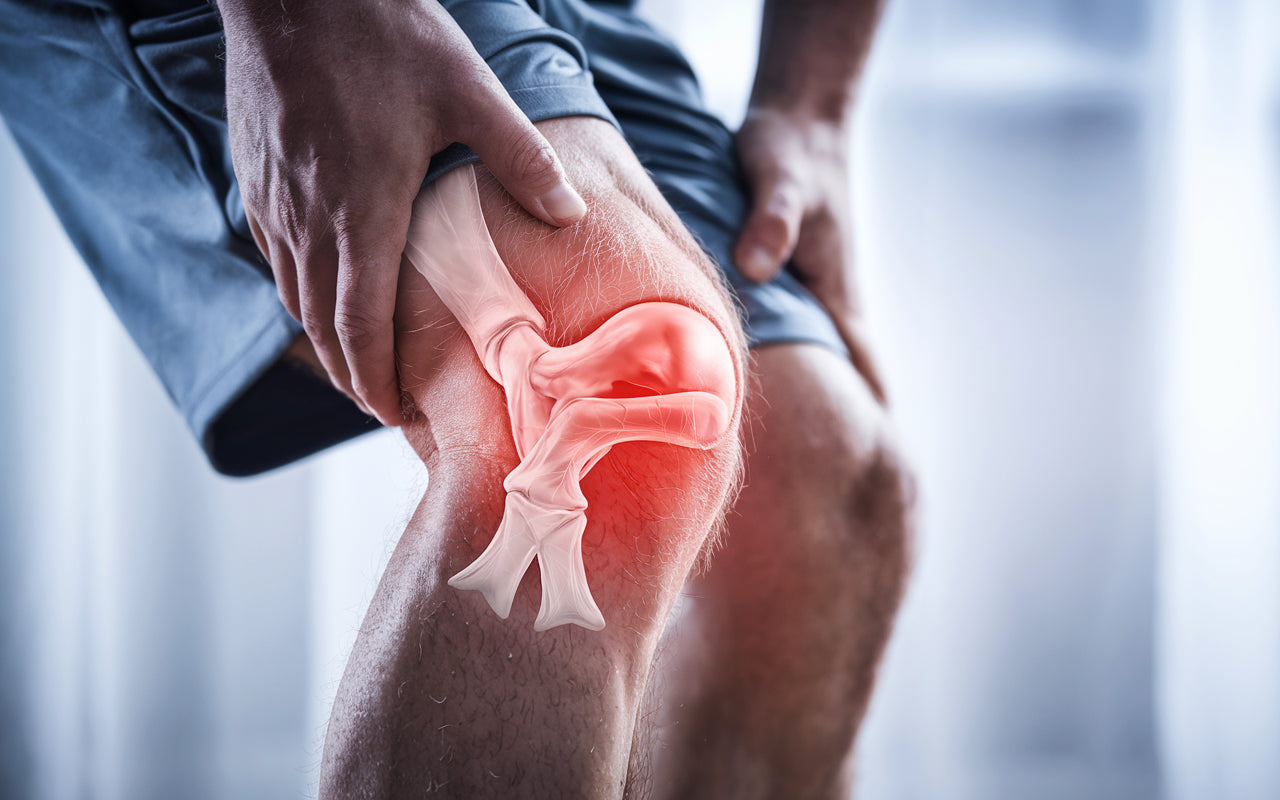
A cruciate ligament injury is one of the most serious knee injuries that can affect athletes and active people. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cruciate ligament injuries, their symptoms, treatment options, and how the right knee brace can help in the rehabilitation process.
What is a cruciate ligament injury?
The cruciate ligaments in the knee joint consist of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). These ligaments form an X in the knee joint and play a crucial role in the stability of the knee. A cruciate ligament injury occurs when one of these ligaments is damaged or torn, often in connection with high-intensity or contact sports, such as in an ACL injury (anterior cruciate ligament injury) .
Anterior cruciate ligament injury vs. Posterior cruciate ligament injury
Anterior cruciate ligament injury: More common than posterior injuries and often linked to sudden movements or hyperextension of the knee.
Posterior cruciate ligament injury: Occurs more often with direct trauma, such as in car accidents when the lower leg is pressed against the dashboard. For more information on symptoms and diagnosis, see Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury .
Symptoms of cruciate ligament injury
Typical symptoms of an anterior cruciate ligament injury include:
- Pain and swelling that comes on quickly
- Feeling that the knee is unstable
- Difficulty walking up stairs or fully extending the leg joints
- Often an audible sound when a cruciate ligament ruptures
If a cruciate ligament injury is suspected, a doctor's visit is recommended for referral for further examination. These symptoms may be similar to those of an unstable knee , which should also be considered in the diagnosis.
Degrees of cruciate ligament injuries
Cruciate ligament injuries are classified into three degrees depending on the extent of the injury:
- Grade 1: Minor injury with local pain, but limited functional impairment
- Grade 2: Major injury with instability and some knee dysfunction
- Grade 3: Complete rupture of the cruciate ligament with extensive instability and functional impairment
Sometimes swelling occurs as one of the first signs, which is also common with a swollen knee .
Symptoms of posterior cruciate ligament injury
The symptoms of a posterior cruciate ligament injury can vary in intensity. ACL injury symptoms and ligament injury symptoms often overlap, but there are some specific signs of a torn cruciate ligament in the knee:
- Pain – often located at the back of the knee
- Swelling after the injury (hemarthrosis)
- Instability, especially when walking up stairs
- Movement restriction
- Tenderness to the touch
- Stiffness after inactivity
Similar symptoms can occur withknee overload , which can delay diagnosis.
Treatment of cruciate ligament injury
The best treatment for an ACL injury depends on the severity of the injury and the individual's activity level and goals. The goal of all treatment is to restore stability, mobility, and function to the knee, as well as to prevent future injuries.
Treatment can be both conservative (without surgery) and surgical, often in combination with rehabilitation, physiotherapy and supportive aids.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment focuses on physiotherapy, strengthening exercises and gradual rehabilitation. The goal is to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and regain stability without surgery.
This method is particularly suitable for less serious injuries or people with lower activity levels.
Surgical reconstruction
In more serious injuries, surgical reconstruction may be necessary. During the procedure, the damaged cruciate ligament is replaced with a tendon, often from the patient's own body.
The surgery aims to restore the stability of the knee and enable a return to sports or high-level physical activity.
Knee pads (e.g. Knee Comfort™)
A knee brace offers extra support and stability during both training and everyday life, reducing the risk of further injuries.
Knee Comfort™ can be used regardless of the treatment method – both during rehabilitation and after surgery – to relieve the joint and improve safety during movement.
The PRICE principle
PRICE stands for Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression , and Elevation .
These measures are often used immediately after the injury to relieve pain, reduce swelling, and protect the knee from further strain.
Pain relief
Pain relief may include anti-inflammatory medications, heat therapy, or other medical methods that facilitate rehabilitation.
This is often used in combination with exercises and supportive aids for optimal recovery.
Important to consider
Rehabilitation after an ACL injury requires patience and continuity. Regular exercise and the correct use of knee pads can speed up recovery and reduce the risk of future problems.
In case of persistent instability or pain, you should always consult a physiotherapist or orthopedist.
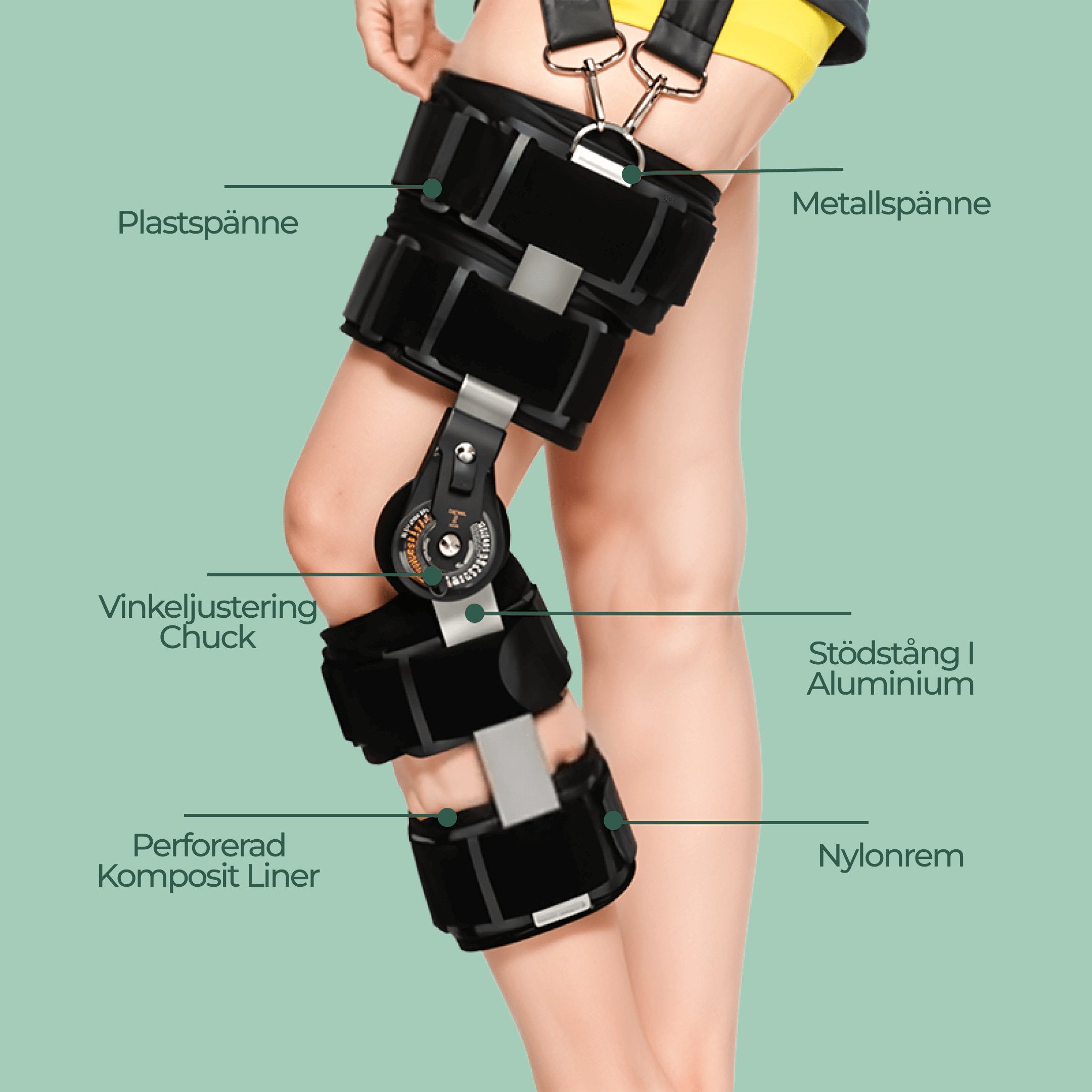
Knee Comfort™ – for effective cruciate ligament injury rehab
- Provides extra support for damaged anterior cruciate ligament
- Helps stabilize the knee and reduces unnecessary strain
- Can be used both before and after possible cruciate ligament surgery
With the right rehabilitation and aids, many sufferers can regain a normal level of activity and prevent re-injury to the cruciate ligament. Regular follow-up and adapted training are the key to a sustainable recovery.
Knee Comfort™ contributes to increased safety in everyday life and during training. It gently compresses the joint, reduces swelling and provides the right biomechanical support – something that can be crucial in the first months after the injury.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of cruciate ligament injuries, you can:
- Perform regular strength training
- Improve landing technique and movement awareness
- Include balance and coordination exercises
- Using the right equipment, including knee pads
For preventive purposes , PFSS (patellofemoral pain syndrome) can also be prevented through the same type of training.
Summary and advice for cruciate ligament injuries
A cruciate ligament injury requires careful diagnosis and structured rehabilitation. A knee brace like KnäKomforten™ can provide extra stability and reduce the risk of new injuries. By following a planned treatment, it is possible to return to normal activity. This also applies to conditions such as meniscus injury , which sometimes occur simultaneously.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long is the recovery time after a cruciate ligament injury?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and the chosen treatment method. With conservative treatment, it can take 3-6 months before you can return to full activity. After surgical reconstruction, rehabilitation can take 6-12 months before you can return to sports at the same level as before the injury. Using the Knee Comfort™ during rehabilitation can contribute to a more effective and safe recovery process.
Can I exercise with a cruciate ligament injury?
Yes, but it is important to adapt training to the injury. During the acute phase, focus should be on reducing swelling and regaining mobility. After that, strength training and balance exercises can be gradually introduced under the supervision of a physiotherapist. Activities that involve rapid twisting or jumping should be avoided until the knee is fully rehabilitated. KneeComfort™ can provide extra support and security during training.
How effective is Knee Comfort™ in preventing cruciate ligament injuries?
The Knee Comfort™ can be an effective tool to reduce the risk of ACL injuries, especially when returning to sports after a previous injury. It provides extra stability to the knee joint and can help prevent overextension. However, it is important to remember that a knee brace is not a substitute for proper training and technique. It should be used as part of a comprehensive prevention strategy that includes strength training, balance exercises and a proper warm-up.

