Swollen Knee: Causes and Treatment
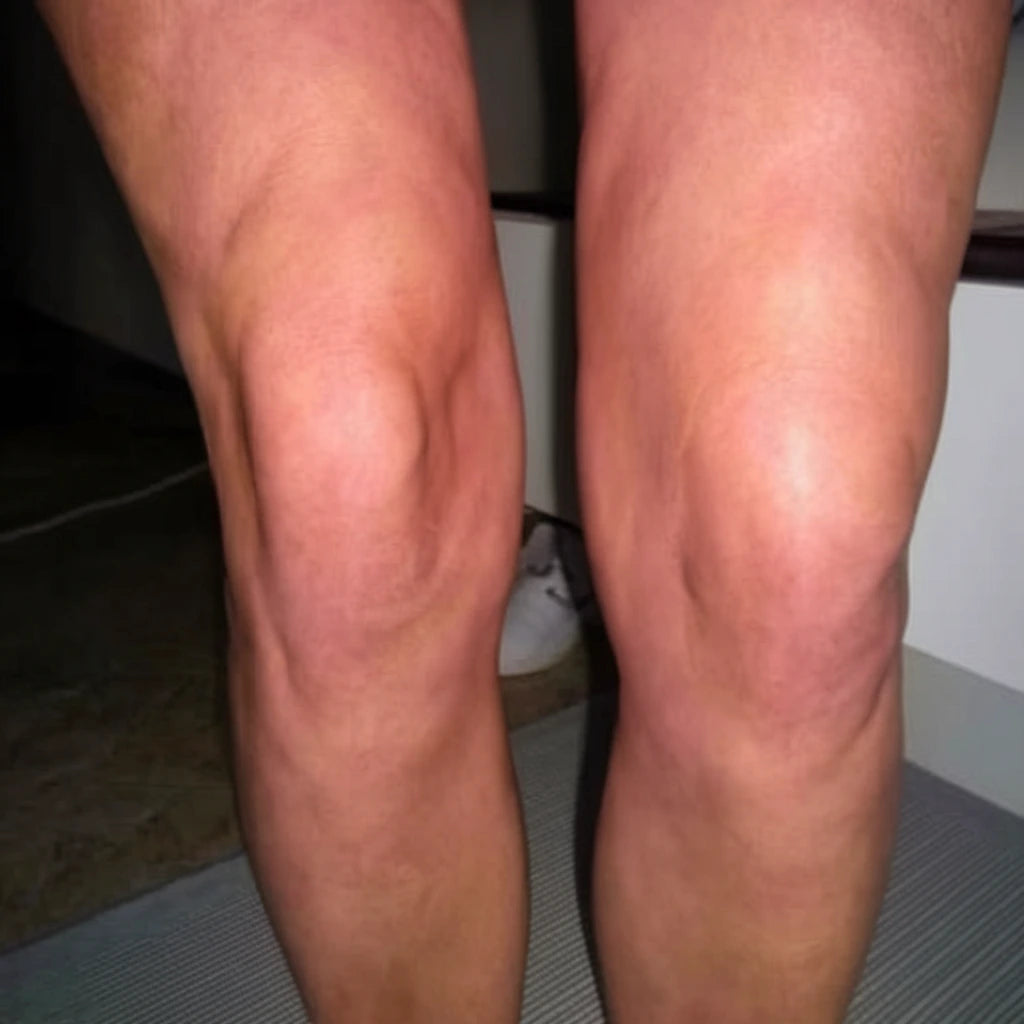
Knee swelling, also known as knee effusion or "water on the knee," is a common problem that can cause discomfort and limited mobility. This condition occurs when excess joint fluid builds up in or around the knee joint, leading to a swollen, fluid-filled knee. When the knee swells, both function and comfort are affected, and many people find that bending or putting weight on the knee can be painful. Fluid in the knee can develop quickly or gradually, depending on the underlying cause.
Water in the Knees: Common Symptoms
Symptoms of fluid in the knee vary depending on the cause, but swelling, tenderness, and limited movement are common. The knee often feels stiff, especially after rest or in the morning. With more extensive fluid accumulation, it may be difficult to bend or fully extend the leg. The pain often worsens with weight bearing. A common condition that can occur along with swelling is a clicking sound in the knee , which indicates changes in the joint structure.
In some cases, it may be difficult to fully bend or extend the knee, affecting the ability to walk, run, or participate in sports. The swelling can sometimes extend to the kneecap and down the leg. If the knee swells rapidly after an injury, such as a swollen knee after a fall, it is especially important to seek medical attention. In the case of a swollen kneecap, symptoms may include localized tenderness and a visible bulge at the front of the knee.
Causes of swollen knee
Knees can swell for several reasons. Common are injuries to the meniscus, cruciate ligaments or ligaments – especially after sports or a fall. Overuse, osteoarthritis or inflammation can also cause swelling. Infections and rheumatic diseases can cause acute fluid accumulation and often require rapid treatment. Chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis of the knee joint develop gradually and cause recurrent swelling.
Diagnosis and treatment for swelling in the knee?
To determine the cause of water in the knee, a medical assessment is often required. Examinations such as X-rays, ultrasounds or MRIs may be necessary. In some cases, fluid is removed from the knee for analysis. Treatment depends on the underlying cause, but common measures include rest, ice, compression and elevation to reduce knee swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs are used for inflammation. In conditions such as knee inflammation, cortisone injections or physiotherapy may also be necessary, especially to reduce knee swelling after injury or overuse.

Prevent fluid in the knee with Knee Comfort™
Preventive measures to reduce the risk of fluid in the knee include maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joint, strengthening the muscles around the knee through regular exercise, and using proper technique and protective equipment during physical activities.
For people with recurring problems with swollen knees, it is important to:
- Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms
- Take breaks during activities that put stress on the knee
- Use inserts in your shoes if poor posture is contributing to the problem
- Don't ignore early symptoms of overload
An effective preventative solution is KnäKomforten™, a specially designed knee brace that provides support and relief for the knee joint. KnäKomforten™ uses advanced compression technology to help prevent fluid from accumulating in the knee during activity. It provides stability and reduces stress on the knee joint, making it ideal for both preventative use and for ongoing problems with fluid in the knee. Many users report that regular use of KnäKomforten™ has helped them return to physical activities with reduced risk of swelling and discomfort.
What does recovery look like for knee swelling?
Recovery time for fluid in the knee varies depending on the cause and recommended treatment. With proper care, many types of knee effusion can resolve within a few weeks, but they can recur if they are the result of a chronic condition such as osteoarthritis.
For sports injuries that cause a swollen knee with fluid, it is important to allow the knee to fully recover before returning to full activity. Returning too soon can worsen the injury and lead to long-term problems.
When should you seek medical attention for a swollen knee?
It is important to seek immediate medical attention if:
- You can't put any weight on your knee at all.
- There is no sensation or pulse below the knee.
- Knee feels unstable or "gives way"
- You have a fever along with a swollen knee, which may indicate infection
- The swelling is extreme and occurred suddenly
- Knees are very red and warm, which may indicate inflammatory conditions
These symptoms may indicate more serious conditions that require immediate medical attention, and an orthopedist should be consulted.
Summary
Swollen knees are a common problem that can be caused by injuries, inflammation, or chronic conditions. Correct diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. By paying attention to your body's signals, preventing overuse injuries, and seeking help early, you can reduce the risk of long-term problems. Learn more about conditions like knee bursitis , which can also cause swelling and discomfort.
Frequently asked questions about water in the lap
What should you do if you have a swollen knee?
If you experience swelling in your knee, it is important to first rest the affected leg. Apply ice to the knee in 20-minute intervals to reduce swelling and relieve pain. Compression with an elastic bandage can also help, as can keeping the knee elevated. If the swelling persists, is very painful, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or an inability to bear weight on the knee, you should seek medical attention.
Can fluid in the knee go away on its own?
In some cases, small amounts of fluid in the knee can be absorbed by the body without medical treatment, especially if it is caused by a minor injury or overuse. However, it is important to identify the cause of the fluid. If the fluid is the result of a more serious injury or underlying condition, medical intervention may be needed to treat the underlying cause.
What do you do about inflammation in the knee?
Treatment for knee inflammation depends on the specific cause but may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs, may be recommended to reduce pain and swelling. In some cases, physical therapy may be necessary to strengthen the knee and improve its function. If the inflammation is due to an underlying condition, such as rheumatoid arthritis, more specific treatment may be required.
Is it good to walk when you have knee pain?
Mild to moderate walking can be good for your knee if it doesn't cause increased pain or swelling. Walking helps keep the joint mobile and can strengthen the muscles around the knee. However, it's important to listen to your body and adjust your activity level so that it doesn't aggravate your symptoms. If walking hurts, try reducing the intensity or length of your walk or discuss alternative exercises with a physical therapist.
Can you exercise to remove fluid from your knee?
Exercise itself will not directly "work out" fluid in the knee joint, but it can help reduce inflammation and improve circulation, which can lead to fluid loss. Specific exercises recommended by a physical therapist can strengthen the muscles around the knee and support the healing process. It is important to avoid exercises that put too much strain on the knee and instead focus on low-intensity exercise that does not aggravate swelling or pain.

